
Digital Request for Payments presenting Recurring Invoices
Using Digital Request for Payments presenting Recurring Invoices
 Digital Request for Payments presenting Recurring Invoices and recurring Real-Time instant payments, are defined simply as: Irrevocably collected funds in a Payee bank account and usable immediately by the owner of the account. An upfront on-time 'standing approval' using Digital Request for Payments presenting Recurring Invoices is an instruction or set of instructions a Payer uses to pre-authorize their financial institution to pay future Request for Payments, RfPs without requiring the Payer to review and approve each RfP.
Digital Request for Payments presenting Recurring Invoices and recurring Real-Time instant payments, are defined simply as: Irrevocably collected funds in a Payee bank account and usable immediately by the owner of the account. An upfront on-time 'standing approval' using Digital Request for Payments presenting Recurring Invoices is an instruction or set of instructions a Payer uses to pre-authorize their financial institution to pay future Request for Payments, RfPs without requiring the Payer to review and approve each RfP.
Attributes of Digital Request for Payments presenting Recurring Invoices for your business using instant payments
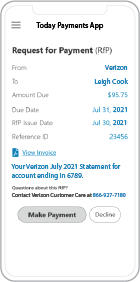
When presenting recurring invoices through Digital Request for Payments (RfP), several key elements should be included to ensure clarity, accuracy, and ease of payment for both the payer and the payee. Here are the essential elements of presenting recurring invoices via RfPs:
1. Invoice Header: Clearly display the invoice header containing essential information such as the invoice number, issue date, due date, and payment terms. This provides context and helps the payer understand the urgency and expectations regarding payment.
2. Payer and Payee Details: Include detailed information about the payer and the payee, including their names, addresses, contact information, and any relevant identification or account numbers. This ensures that the invoice is correctly addressed and facilitates communication between the parties.
3. Itemized Charges: Present a breakdown of all goods or services provided in the recurring invoice, including descriptions, quantities, unit prices, and total amounts for each line item. Itemizing charges helps the payer understand the invoice components and verify the accuracy of the billing.
4. Total Amount Due: Clearly indicate the total amount due for the recurring invoice, including any applicable taxes, fees, or discounts. Highlighting the total amount due ensures that the payer can easily identify the payment obligation.
5. Payment Instructions: Provide clear and concise instructions on how the payer can make the payment. Include accepted payment methods (e.g., bank transfer, credit card, digital wallets), payment deadlines, and any required payment references or codes. This guides the payer through the payment process and reduces the likelihood of payment errors.
6. Recurring Payment Schedule: Clearly outline the recurring payment schedule, including the frequency (e.g., monthly, quarterly, annually), start date, end date (if applicable), and the total number of recurring payments. Communicating the payment schedule helps the payer anticipate future payments and plan accordingly.
7. Authorization: Include language indicating that the payer authorizes the payee to initiate recurring payments according to the specified schedule. This authorization should be clear and explicit, outlining the terms and conditions of the recurring payment arrangement.
8. Terms and Conditions: Provide comprehensive terms and conditions governing the recurring payment arrangement, including cancellation policies, late payment penalties, dispute resolution procedures, and any other relevant terms. This ensures that both parties are aware of their rights and responsibilities regarding recurring payments.
9. Compliance and Security: Ensure compliance with relevant legal and regulatory requirements, including data privacy laws, financial regulations, and industry standards. Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive financial information and prevent unauthorized access or fraud.
10. Contact Information: Include contact information for the payee's customer support or billing department. This allows the payer to reach out with any questions or concerns regarding the invoice or payment process.
By including these elements in recurring invoices presented through Digital Requests for Payments (RfPs), businesses can streamline the payment process, improve transparency, and enhance the overall invoicing experience for both parties involved.
Creation Recurring Request for Payment
We were years ahead of competitors recognizing the benefits of RequestForPayment.com. We are not a Bank. Our function as a role as an "Accounting System" in Open Banking with Real-TimePayments.com to work with Billers to create the Request for Payment to upload the Biller's Bank online platform. Today Payments' ISO 20022 Payment Initiation (PAIN .013) shows how to implement Create Real-Time Payments Request for Payment File up front delivering a message from the Creditor (Payee) to it's bank. Most banks (FIs) will deliver the message Import and Batch files for their company depositors for both FedNow and Real-Time Payments (RtP). Once uploaded correctly, the Creditor's (Payee's) bank continues through a "Payment Hub", either FedNow or RTP, will be the RtP Hub will be The Clearing House, with messaging to the Debtor's (Payer's) bank.
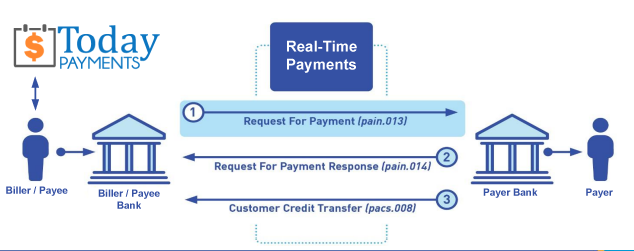
ACH and both Instant and Real-Time Payments Request for Payment
ISO 20022 XML Message Versions
The versions that
NACHA recommends for the Request for Payment message and the Response to the Request are pain.013 and pain.014
respectively. Version 5 for the RfP messages, which
The Clearing House Real-Time Payments system has implemented, may also be utilized as
there is no material difference in the schemas. Predictability, that the U.S. Federal Reserve, via the
FedNow ® Instant Payments, will also use Request for Payment. The ACH, RTP ® and FedNow ® versions are Credit Push Payments.
Payees ensure the finality of Instant Real-Time
Payments (IRTP) and FedNow using recurring Requests for
Payments (RfP), Payees can implement certain measures:
1.
Confirmation Mechanism:
Implement a confirmation mechanism to ensure that each
payment request is acknowledged and confirmed by the payer
before the payment is initiated. This can include requiring
the payer to provide explicit consent or authorization for
each recurring payment.
2.
Transaction Monitoring:
Continuously monitor the status of recurring payment
requests and transactions in real-time to detect any
anomalies or discrepancies. Promptly investigate and resolve
any issues that arise to ensure the integrity and finality
of payments.
3.
Authentication and
Authorization: Implement strong
authentication and authorization measures to verify the
identity of the payer and ensure that only authorized
payments are processed. This can include multi-factor
authentication, biometric verification, or secure
tokenization techniques.
4.
Payment Reconciliation:
Regularly reconcile payment transactions to ensure that all
authorized payments have been successfully processed and
finalized. This involves comparing transaction records with
payment requests to identify any discrepancies or
unauthorized transactions.
5.
Secure Communication Channels:
Utilize secure communication channels, such as encrypted
messaging protocols or secure APIs, to transmit payment
requests and transaction data between the payee and the
payer. This helps prevent unauthorized access or
interception of sensitive payment information.
6.
Compliance with Regulatory
Standards: Ensure compliance with
relevant regulatory standards and guidelines governing
instant payments and recurring payment transactions. This
includes adhering to data security requirements, fraud
prevention measures, and consumer protection regulations.
By implementing these measures, Payees can enhance
the finality and security of Instant Real-Time Payments
using recurring Requests for Payments, thereby minimizing
the risk of payment disputes, fraud, or unauthorized
transactions.
Each day, thousands of businesses around the country are turning their transactions into profit with real-time payment solutions like ours.

Contact Us for Request For Payment payment processing

